Accounts Receivable Aging Report: Definition and How To Use It

No matter what industry you’re in, keeping track of unpaid invoices is an essential part of maintaining a healthy cash flow. An accounts receivable aging report is a financial reporting tool that does just that, letting you see unpaid invoice balances, along with the duration for which they’ve been outstanding.
Your accounts receivable aging report (also called an AR aging report) helps your business identify, track, and manage your open invoices. It’s an important tool for getting paid promptly and ensuring you follow up with slow-paying clients. In this guide, we’ll explain the method of AR aging reports, provide an overview of the aging schedule, and explain how to prepare an accounts receivable aging report.
Key Takeaways
- Accounts receivable aging reports help you track, manage, and follow up with overdue payments from clients.
- AR aging reports separate receivables into ‘buckets,’ which categorize the total balance outstanding based on how many days passed since an invoice was issued.
- AR aging reports also help you change credit policies, adjust client relationships, avoid bad debts, address doubtful accounts, and improve cash flow.
- Accounting software is a fast, easy way to create useful AR aging reports.
Table of Contents
- What Is an Accounts Receivable Aging Report?
- What Information Does an Accounts Receivable Aging Report Contain?
- Why Are Aging Reports Important?
- How to Prepare an AR Aging Report
- Accounts Receivable Aging Report Example
- How Is Aging of Accounts Receivable Used?
- Utilize Accounts Receivable Aging Reports To Optimize Cash Flow
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Is an Accounts Receivable Aging Report?
An accounts receivable aging report is a type of financial report that provides an overview of all accounts receivable—sales made by the business for which payment has not yet been received. The report organizes all accounts receivable according to the length of time that the payment has been outstanding. In other words, it shows the ‘age’ of each account.
Account receivables arise when a business provides goods or services on a credit—meaning that payment will be made after you make the sale and issue an invoice. Businesses can decide how long to allow accounts to remain open.
For example, you may allow clients to pay for goods 30 days after they’re delivered. This represents an asset to your business since you’ll be receiving payment in the future.
In a perfect world, you’d always receive payments on time. Unfortunately, it’s common for clients to be late with payment, either due to forgetfulness or other issues. When you make a lot of sales, it’s important to have a tool to keep track of receivables. That’s the purpose of an AR aging report. It helps you to minimize uncollected debts, ensuring steady cash flow and identifying potential losses from clients.
To identify the average age of receivables and to identify potential losses from clients, businesses regularly prepare accounts receivable aging reports. This allows them to collect these bills as soon as possible to move the money into the bank account.

What Information Does An Accounts Receivable Aging Report Contain?
Your AR aging report will contain all of your outstanding invoices separated into due-date categories. This not only makes it easier to track all of your accounts receivable in one place but also gives you insight into customers who are late with their payments.
The accounts receivable aging report is separated into day-range columns to indicate how far past due each payment is. You can create ranges for this depending on your business’ payment due date policies, but the most common format is to separate them as follows:
- Current: Invoices not past due
- 1-30 days: Past due for 1–30 days
- 31-60 days: Past due for 31–60 days
- 61-90 days: Past due for 61–90 days
- 91+ days: Past due for 91 or more days
Why Are AR Aging Reports Important?
AR aging reports are important because they ensure your business gets paid on time for the goods or services you provide.
If your business, like many others, operates on credit, regular accounts receivable aging reports will help you stay on top of late payments, helping to keep your cash flow steady and ensuring you steer clear of financial difficulties.
There are many other benefits to regular AR aging reporting, including:
1. Staying In Touch with Overdue Accounts
Accounts receivable aging reports are a useful tool for ensuring you are regularly reviewing clients’ accounts and informing them about their outstanding balances, as well as giving you a chance to remind them of your billing and collection process. The information from this report will help you create collection letters, and a copy of the report itself might be attached as well.
2. Re-evaluating Practices and Policies
Your AR aging report is a useful tool when deciding whether to adjust your practices and policies for selling and extending credit to clients, such as only accepting cash sales. These changes can be made for all of your accounts or could be implemented for only high-risk customers who regularly struggle to make payments on time.
3. Changing Supplier Payment Terms
Since overdue accounts hold up cash flow, the AR aging report can be used to make sure your outstanding payments don’t create an issue with suppliers. Depending on your financial position, you may request a credit balance extension or another payment term adjustment depending on how many outstanding payments you’re waiting to receive.
4. Ending Client Relationships
If you’re looking to sever ties with a client who regularly fails to make their payments on time, a history of outstanding receivables, indicated by AR aging reports, can act as evidence to show that you have a good reason to do so.
5. Avoiding Bad Debts
Bad debts are outstanding credit sales accounts that the business will not be able to collect. While these are a fact of life, businesses naturally want to avoid them whenever possible. Consistent accounts receivable aging reporting will help you prevent an overdue credit balance from becoming a bad debt expense.
6. Writing Off Bad Debts
If you do end up incurring a bad debt expense, you’ll need to provide evidence in the form of accounts receivable aging reporting (along with other documentation). This is required to deduct it from your income tax.
7. Setting Invoice Factoring Rates
If your business chooses to factor in outstanding invoices (i.e., sell debts from credit sales for someone else to collect), AR aging reports are a necessary piece of documentation. These reports will help your factoring company set the factoring rate.
How To Prepare Accounts Receivable Aging Report
Your AR aging report is an essential part of cash flow management for your business if you work with credit sales. Fortunately, it’s a fairly simple financial statement to create—you can do it in just four steps:
1. Gather Unpaid Invoices
First, you’ll need to collect and organize all outstanding invoices from your accounts receivable. This means any invoices with a balance, even if it’s just a partial balance.
2. Calculate the Number of Days Past Due
Next up, determine how many days past due each invoice is. For instance, if payment was due on January 15th, and it’s now January 25th, you would mark it as being 10 days past due. You can record this in a spreadsheet to help make the next step simpler.
3. Categorize Invoices
Next, organize all unpaid invoices for each customer according to your chosen aging schedule. Think of each category as a ‘bucket’ to place your invoices into. The most common of these buckets would be ‘current’ (unpaid invoices that aren’t past due), ‘1-30 days past due,’ ‘31-60 days past due,’ and so on. You will list the total amount for each bucket.
For example, say that you have a client with 2 outstanding invoices. One invoice is for $1,000 and is 14 days past due, and the other invoice is for $1,800 and is 21 days past due, you would write it as: ‘1-30 days past due: $2,800.’
4. Make an Aging Schedule
The final step is to repeat the process from step 3 for all of your clients having unpaid invoices on their accounts. When this is done, you’ll be able to see each ‘bucket’ of overdue payments, giving you a much clearer sense of how much you’re owed for each client and how overdue your accounts are in general.
Accounts Receivable Aging Report Example
Your accounts receivable aging report should be legible, organized, and easy to interpret. Here’s an example of a formatted AR aging report—make sure yours looks similar to the picture below to ensure it has all the information you need:
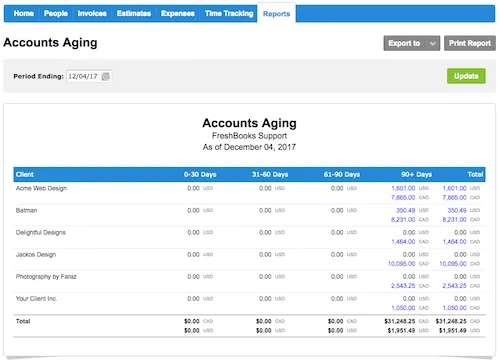
How Is Aging of Accounts Receivable Used?
Your AR aging report can be used for several purposes beyond simply showing you how effective your collection process is. Other uses for this report include:
Adjusting Credit Policies
The aging schedule is used to identify clients that are late in paying their invoices. If the bulk of your overdue amounts is attributable to a single client, your business can take the necessary steps to ensure that the customer’s account is collected promptly.
If there are several customers with overdue amounts that extend beyond 60 days, it may signal the need to tighten your credit policy toward existing and new clients.
Identifying Cash Flow Problems
The aging schedule also identifies any recent changes or new problems in accounts receivable. This can provide the necessary answers to protect your business from cash flow problems.
Calculating the Allowance for Doubtful Debts
The accounts receivable aging method is used to estimate the amount of uncollectible debts for companies that operate on credit sales and is usually used by companies with thousands of collections and that use the accrual accounting method. Allowance for doubtful debts includes the approximate amount of receivables that may not be collected. This is used as an ending balance of allowance for doubtful accounts.
While the percentage is different for each group and is based on past experience and current economic conditions, the general rule of thumb is that the longer an account receivable remains outstanding, the lower the chances of its collection.
At the end of each accounting period, the adjusting entry should be made in the general journal to record bad debt expenses and doubtful accounts. Compute the total amount of estimated uncollectible debts and then make the adjusting entry by debiting the bad debts expense account and crediting allowance for doubtful accounts.
Utilize Accounts Receivable Aging Reports To Optimize Cash Flow
Without an accounts receivable aging report, it can be difficult to maintain a healthy cash flow and identify potentially bad credit risks to your business posed by doubtful accounts. To be useful, your report needs to include client information, the status of collection, the total amount outstanding, and the financial history of each client.
Looking for a fast, easy way to create these reports? The best method is with accounting software that lets you customize client settings, send automatic payment reminders, and get paid sooner. Try FreshBooks free.

FAQs About AR Aging Reports
More questions about creating, reading, and using accounts receivable aging reports? Here are more questions about this type of income statement:
Why do I need an aging report?
Your AR aging report lists your business’ outstanding invoices, making it much simpler to track and manage overdue payments. This lets you improve your collection process, rethink payment terms, prevent doubtful accounts from becoming bad debts, and generally improve your cash flow by efficiently collecting what your clients owe.
What’s considered a good AR aging percentage?
Your AR aging percentage should be as low as possible—10 to 15% is ideal, but this can differ from business to business. You can find this number by taking the total amount of accounts receivable overdue in each of the overdue buckets by the total amount of receivables outstanding.
How do you calculate aging for accounts receivable?
To calculate AR aging, look at how many days past due an outstanding invoice is. Then, place it in the appropriate category (e.g., 1-30 days past due, 31-60 days past due, etc.). Then, add up all amounts due in each category to calculate the overdue payments for each bucket.
What is an aging schedule?
Your aging schedule is simply the categories you choose to place aging accounts receivable into. An example of an aging schedule would be ‘Current,’ ‘1-30 days past due,’ ‘31-60 days past due,’ and so on. Depending on your policies, you can adjust these ranges as you see fit.
How do I create an AR aging report?
The best way to create a useful accounts receivable aging report is with accounting software that uses automation and intelligent features to make tracking overdue payments simple. Accounting software also helps you get paid faster with automatic reminders sent to clients.
Reviewed by
Sandra Habiger is a Chartered Professional Accountant with a Bachelor’s Degree in Business Administration from the University of Washington. Sandra’s areas of focus include advising real estate agents, brokers, and investors. She supports small businesses in growing to their first six figures and beyond. Alongside her accounting practice, Sandra is a Money and Life Coach for women in business.
RELATED ARTICLES


 How to Make a Profit and Loss Report?
How to Make a Profit and Loss Report? Accounting Reports: Definition And 3 Types
Accounting Reports: Definition And 3 Types How to Write a Profit and Loss Statement?
How to Write a Profit and Loss Statement? Monthly Financial Reports: What Are They And How to Read
Monthly Financial Reports: What Are They And How to Read What Is Financial Reporting? Definition, Importance, and Types
What Is Financial Reporting? Definition, Importance, and Types Expense Report: What It Is and Why Is It Important?
Expense Report: What It Is and Why Is It Important?